ORIGINAL RESEARCHES
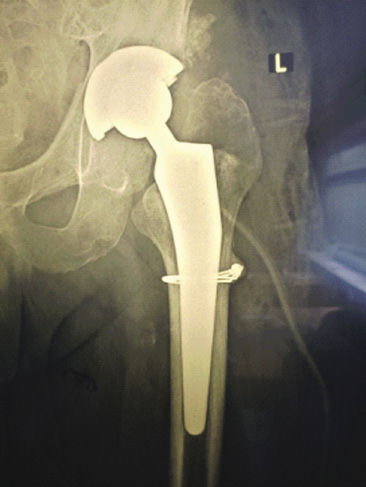
Introduction. The increase in the number of patients with joint and hip diseases is an actual problem in the clinical medicine. Objective: to improve outcomes of the combined surgical treatment of patients with deep periprosthetic infection (PPI) by developing and improving surgical techniques using spacers and laser technologies.
Material and methods. Thirty-five patients with suppurated large joints as a complication after their replacement were examined and treated. In 9 (25.7 %) patients, PPI developed within 3–12 months after the primary arthroplasty. Twenty (57.1 %) patients developed PPI within 1–2 years after the surgery. In 4 (11.4 %) cases, suppuration in the endoprosthetic area developed in 2–3 years, and in 2 (5.7 %) patients – in 3–3.5 years. The age of the patients was 47–70 years. The main group consisted of 20 patients, the control group – of 15 patients. Patients from the main group had laser photodynamic therapy (PDT) session after the removal of endoprosthetic elements and devitalized tissues.
Results. Patients from the main group had uneventful postoperative course – less pain syndrome, rapid resolution of the infl ammatory process, wound healing by the primary tension.
Conclusion. Application of a new intraoperative PDT technique, developed by the authors, promotes rapid resolution of purulent-infl ammatory process and better healing of postoperative wounds by primary tension.
Abstract
Changes related to COVID-19 have been made to the International Classifi cation of Diseases of the Tenth Revision (ICD-10) – a separate code has appeared to describe the postcoid syndrome.he neurosomatic status of patients who had COVID-19 is characterized not only with clinical manifestations of the disease but also with complaints of cerebral, cardiac and general somatic nature. Moreover, they are combined with severe personal and reactive anxiety as well as moderate cognitive impairments and low level of satisfaction of patients with their condition.
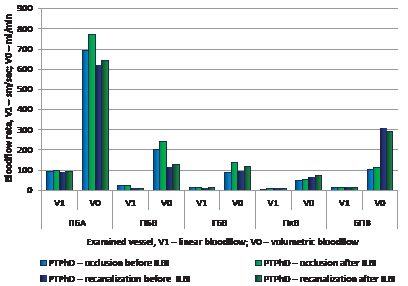
Post-thrombophlebitis of lower extremities occurs in 14–29 % of cases and develops within the fi rst two years after the episode of deep vein thrombosis of lower extremities in 20–50 % of patients. Objective: to apply intravenous laser blood irradiation (ILBI) for optimizing outcomes in patients with post-thrombophlebitic disease of their lower extremities. Materials and methods. 52 patients were treated with ILBI. They were randomized into two groups by the following clinical criteria: stage of occlusion – 18 patients (Group 1) and stage of recanalization – 34 patients (Group 2). ILBI course included 7 sessions: irradiation power – 3–15 mW, pulse frequency – 80–3000 Hz, exposure time – 5–15 minutes. Parameters of venous outfl ow and inguinal lymph nodes were monitored by ultrasound examination. Radial immunodiffusion was used to determine levels of IgG, IgM and IgA in blood plasma and serum; turbidimetry – to determine immune complexes; T-lymphocytes – by the receptors to erythrocytes. B-lymphocyte level was monitored with luminescence-serological and complementary rosette formation techniques. Results and discussion. A statistically signifi cant increase in linear and volumetric blood fl ow in great vessels was revealed in both groups. In Group 1, linear blood fl ow in the great saphenous vein increased by 5.2 %; volumetric blood fl ow increased up to 113.0 ± 2.14 mL/min (p < 0.01). In Group 2, volumetric blood fl ow slowed down by 4.1 %. Lymph nodes contracted statistically signifi cantly; the medullary layer narrowed up to 0.32 ± 0.05 cm (p < 0.05), level of IgG, IgM and CIC decreased; number of T-lymphocytes increased up to 60.2 ± 1.7 % (p < 0.05). Conclusion. The revealed effects of intravenous laser blood irradiation at the venous outfl ow, lymph nodes and humoral and cellular immunity in patients with post-thrombophlebitic disease of lower extremities give a reason to recommend the implementation of the discussed technique into a wide clinical practice.
Aim: to study the state of lipid metabolism, hemostasis, inflammatory reaction and the potential for their correction after indirect revascularization in patients with distal steno-occlusion of arteries and critical ischemia of lower extremities (critical ILE).
Material and methods. Changes in hemostasis and dynamics of its parameters during the complex surgical treatment in 131 patients with critical ILE and distal arterial stenoocclusion were analyzed. To achieve the targeted goals, patients were divided into the following groups: 34 patients had traditional care (control group); 32 patients had intravenous laser blood irradiation in combination with standard therapy (Group I); 32 patients had cytokine therapy with roncoleukin in combination with standard therapy (Group II); 33 patients had intravenous laser blood irradiation combined with cytokine therapy and standard therapy (Group III). Parameters of lipid metabolism were studied in dynamics (total cholesterol, very low density lipoproteins, high density lipoproteins, triglycerides); products of lipid peroxidation (malondialdehydes, conjugates, superoxide dismutase); inflammatory mediators (C-reactive protein, sialic acids, seromucoids, fibrinogen A, circulating immune complexes); hemostatic parameters (fibrinogen, fibrinolytic activity, fibrin degradation products, antithrombin III activity). Hemostatic indices were compared with identical parameters of 48 apparently healthy individuals (reference group).
Results. On admission, patients with critical ILE and distal wall occlusion had sharp changes in their lipid metabolism, inflammatory reaction, and hemostasis. Conclusion. The inclusion of intravenous laser blood irradiation and cytokine therapy separately and in combination in a set of therapeutic measures led to the leveling of the studied homeostasis indicators. The best results were obtained in the group where patients had combined perioperative intravenous laser blood irradiation with cytokine therapy in indirect revascularization.
Material and methods. Twenty-two patients with compression-ischemic neuropathy were included into the study. Low-level laser device “ALOK-1” was used for laser therapy. Its beam impacts tissues directly; its power is 1 mW, wavelength – 0.63 μm, spot diameter – 0.8 mkm.
Results. Subjective, objective and instrumental findings became significantly better, if to compare with the pre-operative period.
Conclusion. The developed technique has shown its good efficiency. The intraoperative laser therapy CIN patients decreased the severity of symptoms up to their complete regression; patients were highly satisfied with their postoperative outcomes.
Actuality. Tracheal cancer is a rare disease which amounts up to 0.2% of the total number of cancers. Currently, there is an increase in the number of patients with impaired tracheal patency. Endoscopic procedures are most commonly used to restore and maintain the tracheal lumen. The key treatment for primary cancer is a surgical one; however, due to late diagnostics, the tumor is often inoperable. Chemotherapy for tracheal cancer is ineffective, and practically is not used. At present, endoscopic tracheal recanalization with laser vaporization is a method of choice in patients with inoperable tracheal tumors.
Objective: to improve outcomes in patients with inoperable primary tracheal cancer using Nd-YAG laser either as the fi rst component of staged treatment strategy, or as the fi nal volume treatment.
Methods. Patient K., 75 years old, was admitted to the hospital with complaints of dyspnea at rest, weakness and hemoptysis. As anamnesis showed, the patient had noticed a deterioration in her breathing during the last 6 months. CT scan revealed a volumetric formation (tumor) of the cervicothoracic trachea (8.0 cm above the bifurcation) with 90% stenosing in the lumen. When performing tracheobronchoscopy in the cervicothoracic trachea, a broad-based lumpy tumor, 5 cm long, stenosing the tracheal lumen by 2/3 was found on the posterior wall. Morphological examination of biopsy material revealed adenocystic carcinoma.
Results. The performed endoscopic examination with neodymium YAG laser recanalization demonstrated the advantage of this technique in patients with inoperable tracheal tumors.
Conclusion. Endoscopic recanalization of the trachea with neodymium YAG laser has been proven to be effective in patients with inoperable tracheal cancer. It improves their quality of life as well.
Effects of 1270 nm laser light irradiation at phage particles of virulent klebsiellosis bacteriophage were studied. The medical klebsiellosis bacteriophage, manufactured industrially, was taken as the study object. Klebsiella pneumonia N 296, sensitive to the selected phage, was used as a test-culture. An experimental device manufactured by LTD «New surgical technologies» was used as a source of light. Semiconductor diodes generate light with wavelength 1270 nm (1268–1272 nm) in the continuous mode. The number of viable phage particles in the initial solution of klebsiellosis bacteriophage was 5×108. Irradiation of the phage with 1270 nm laser light decreased the number of viable phage particles to 105. Results did not practically depend on the exposure time, i. e. phage titers were equally reduced when exposed to laser light for 5 min, 10 min and 15 min. Irradiation of Klebsiella bacteriophage with 1270 nm laser light reduced the number of viable phage particles by 3 log orders (initial titer was 108; after irradiation – 105 negative phage colonies). It is indicative of their damage. Mechanisms of phage particle damage should be the object of further research so as to defi ne if laser irradiation with the above mentioned wavelengths can be used in medical practice.
REVIEWS
The given article is a review on the techniques developed for treating purulent disease of fi ngers and hands. This pathology accounts for a considerable part of all pathologies with which patients seek medical care. A high incidence of the disease is determined by a wide range of reasons. Not infrequently, patients come to hospitals after their outpatient treatment, and as a result of long-lasting pathological process, they have to undergo disabling surgeries leading to the loss of a fi nger or even a hand what worsens this problem because of the economic factor. Over the years, medical care for such patients has been constantly developing. Radical changes have taken place not only in the surgical sphere, but also in preoperative one, in postoperative management and in rehabilitation. The technique of treating wounds under sutures with putting a drain-washing system (DWS) has practically become a classical method of choice for managing phlegmons and panaritia. However, like with any other method, there is a number of medical contraindications to it, and, as before, surgeons must treat purulent wounds in fi ngers and hands using open technologies. In addition, results after DWS are often unsatisfactory. For many years, researchers are looking for new approaches to improve not only outcomes of patients’ surgical care but also postoperative management of wounds. Researchers who use laser radiation in their work have repeatedly demonstrated positive results when treating patients with laser light. Highintensity laser irradiation is widely used in medicine; in purulent surgery, it is used as a scalpel for performing necrectomy. Laser light applied for necrectomy signifi cantly improves wound process, accelerates wound healing, promotes early cleansing of the wound defect from fi brin detritus and exudate. Photodynamic therapy (PDT), which has found wide application in oncology, currently is actively used in purulent surgery too because of good outcomes. PDT shortens wound healing, promotes early granulation and formation of soft scars as well as it has the antimicrobial effect at wounds. However, there are very few studies on the application of laser light in patients with purulent diseases of the hand what has impelled the researchers to make trials on laser light and PDT application in the complex treatment of purulent diseases of the hand.
ISSN 2686-8644 (Online)