ORIGINAL RESEARCHES
Purpose. To compare light-oxygen and photodynamic effects at the development of inflammatory reactions caused by histamine so as to study mechanisms of the singlet oxygen effect at biological objects and to optimize their application in clinical practice.
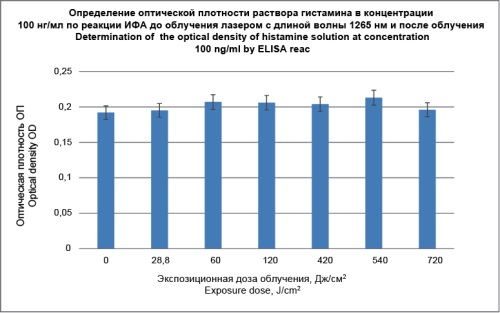
Materials and methods. A domestic diode laser ‘Super Sab’ with λ ≈ 1265 nm (produced by New Surgical Technologies LLC, Moscow, Russia) was used as a source of laser light. 10 female rats of Wistar population weighing 250–300 g were taken in the study. Power density of laser irradiation was 0.25 W/cm2 (exposure dose – 30 J/cm2). Not irradiated scarification sites were used as controls. Histamine concentration in the solution after its irradiation with the same laser was studied by the immunoenzymatic analysis. Photodynamic effect was studied in 12 volunteers; scarification samples with histamine and preliminary applied gel photosensitizer ‘Photoditazine’ were put to them, and the subsequent irradiation with laser light generated by device ‘Atkus-2’ (produced by CJSC ‘Semiconductor Devices, St. Petersburg) having λ ≈ 662 nm, power density 0.3 W/cm2 and exposure dose 50 J/cm2 was made. Scarifications without irradiation were used as controls.
Results. Reliable results (p ≤ 0.01) obtained in the experimental animals revealed the decrease of inflammatory reactions at the irradiated scarification sites with histamine application compared to the controls. While examining the histamine solution irradiated in vitro, no decrease in the histamine concentration was found under different irradiation doses. Histamine tests in volunteers also revealed reliable results (p ≤ 0.05) when the decrease of inflammatory reactions was seen in them after photosensitiser application compared to the controls.
Conclusion. The newly obtained data may clarify some mechanisms of light-oxygen and photodynamic therapy (LOT and PDT); they may also expand indications for clinical application of the discussed therapy and serve as a starting point for future in-depth trials in this direction. One of them, in particular, may be revealing changes in the chemical structure of some important biologically active substances under the impact of LOT and PDT.
Purpose: to develop formulas for selecting parameters for each patient regarding their age and type of appearance by the Fitzpatrick scale. To obtain the formulas after testing the selective micropulse mode by autofluorescent (AF) results would allow to treat patients using the technology of selective micropulse individual retinal therapy (SMIRT) without preliminary testing on serial laser systems.
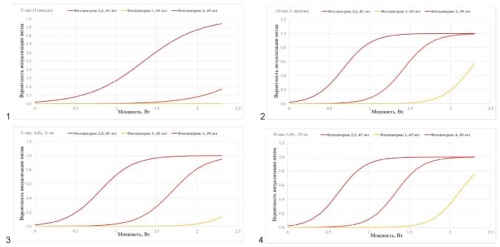
Materials and methods: 97 patients with acute central serous chorioretinopathy, aged 30–65, with type 1 to type 4 appearance by the Fitzpatrick scale were enrolled in the study. The obtained results after the testing of selective micropulse mode (spot diameter – 100 microns, micropulse duration 50–150 μsec, duty cycle – 0.5–5 %, pulse packet duration – from 10 to 50 ms (1–5 pulses per packet), power –1–2 W) were analyzed. Laser system Iridex IQ 577 was used in the trial. For each laser spot, the probability of damage detection (PDD) was calculated with shortwave AF (488 nm) data.
Results. On analyzing 4685 spots by AF findings, PDD logistic regression function was constructed using the likelihood maximization method on a training sample depending on micropulse mode parameters, age and type of appearance by Fitzpatrick scale. The resulting formula was inverted to predict the required power, pulse duration, and number of pulses to achieve the required PDD level. Errors in the logistic regression coefficients were obtained by bootstrapping. The regression quality was assessed using Pearson’s chi-squared test. While comparing the ogistic function and computer modeling, it has been shown that age and type of appearance are key personal characteristics which must be taken into account when selecting parameters of micropulse mode treatment.
Conclusion. The authors have developed formulas for selecting parameters of selective micropulse mode regarding the patient’s age and type of appearance by Fitzpatrick scale without preliminary testing for treatment with SMIRT technique on serial laser systems.
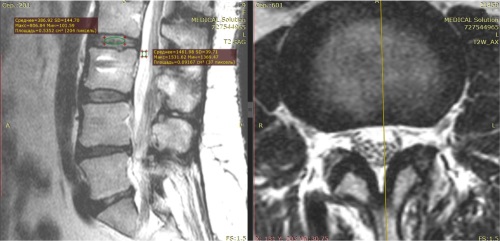
Long-term outcomes (3–5 years) in 71 patient with the adjacent level lesion syndrome (ALDS) were analyzed. All patients underwent minimally invasive surgical interventions (puncture laser decompression of intervertebral discs and radiofrequency denervation of the facet joints) in the neurosurgical department of Irkutsk Scientific Center for Surgery and Traumatology. The applied technology was chosen after analyzing clinical examination findings, introscopy findings, degeneration coefficient and intervertebral disc height.
In the study, there were 37 males, 34 females. Average age 54.1 ± 2.3 years. The time interval between the initial decompression and stabilization surgery and the subsequent minimally invasive surgical intervention was 48 ± 3.8 months.
The effectiveness of minimally invasive surgical treatment was assessed after analyzing clinical and neurological findings, radiological findings (MRI, MSCT, overview and functional spondylography) as well as by the visual analog pain scale and MacNab questionnaire.
COMPARATIVE RESEARCH
Purpose. To make a comparative analysis of the effi ciency of surgical treatment of pilonidal disease with traditional excision and laser destruction.
Materials and methods. 368 patients with pilonidal disease who underwent surgical treatment between 2018 and 2022 were enrolled in the study. The patients were divided into three groups. In Group 1 (n = 112), a cyst was excised, and the wound was tightly sutured with Donatti sutures. In Group 2 (n = 123), patients had Cleft Lift surgery (Bascom II surgery). Group 3 (n = 133) included patients after the combined laser treatment.
Results. The combined laser technique for surgical treatment of pilonidal disease has a statistically signifi cant advantage over traditional surgical methods in terms of surgical time, postoperative pain, length of hospital stay, disability period, healing process, frequency of postoperative complications, and frequency of disease relapses.
Conclusions. The technique of laser destruction and thermoobliteration of coccyx cysts is universal and easy for application, highly effective, provides high quality of life for patients, and can be used routinely in an outpatient setting.
A CLINICAL OBSERVATION
Vulvar lichen sclerosus (VLS) is a chronic inflammatory dystrophic disease affecting the external genitalia, significantly deteriorating the woman’s quality of life and producing an extremely negative effect at her mental status. In case of inefficacy and/or contraindications to traditional pharmacological therapy, modern non-invasive apparatus-based treatment can serve as an alternative. Among them is photodynamic therapy (PDT) which affects targeting tissues with a proper photosensitizing agent and a direct irradiation with light of a specific wavelength. The authors describe their experience in treating 28 patients with VLS who had a course of three PDT sessions. As a result, 82 % of them had a complete symptom remission with no serious adverse effects and excellent therapy tolerance.
ISSN 2686-8644 (Online)