ORIGINAL RESEARCHES
Purpose. To improve the accuracy of diagnosing microcirculation disorders in the intestinal wall tissues in small laboratory animals by introducing hyperspectral imaging in combination with a controlled polychrome LED light source.
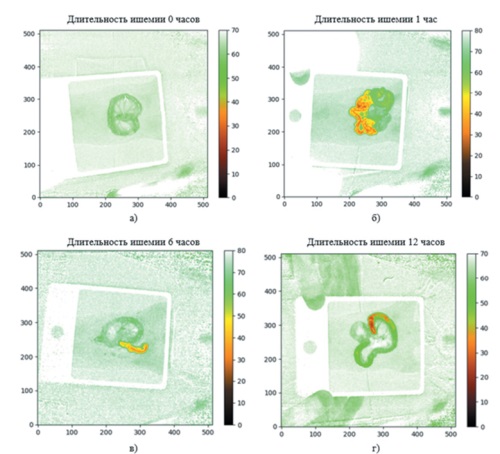
Materials and methods. 10 clinically healthy Wistar rats were used in the study. Intestinal ischemia was modeled by the ligation of mesenteric vessels after laparotomy under inhalation anesthesia. Relaparotomy was performed in 1, 6 and 12 hours. The viability of intestinal tissues and the identifi cation of secondary pathological changes were assessed with the visual Kerte method and a polychrome LED light source providing contrast visualization of biological tissues. Intestinal wall perfusion was assessed by the hyperspectral imaging system. Intestinal resection followed by the sampling for morphological examination was made according to time intervals established by the examination protocol.
Results. Spectral composition of the light source, which reliably detects the intestinal wall necrosis, includes two spectral lines with maxima of λpeak = 503 nm and λpeak = 594 nm at 2:1 intensity ratio. Hyperspectral imaging allowed to get two-dimensional maps of tissue saturation with the following values: 66 ± 2 % (intact tissue), 42 ± 5 % (1 hour), 26 ± 3 % (6 hours) and 21 ± 3 % (12 hours). The performed morphological analysis revealed three key ischemic intervals: 1 hour (ischemia onset), 6 hours (reversible ischemia) and 12 hours (irreversible necrosis). The obtained data confi rm the signifi cant decrease in saturation which correlates with morphological changes, and the effectiveness of the discussed technique for assessing the viability of intestinal tissues.
Conclusion. In the course of the study, the authors have developed a technology for optimizing the lighting during surgery so as to improve contrast imaging of ischemic and necrotic tissue changes. Hyperspectral imaging promotes non-invasive and objective intraoperative assessment of the ischemic damage in the intestinal wall without any exogenous fl uorescent drugs. The obtained results also demonstrate the prospects of introducing optimized lighting and hyperspectral imaging into clinical practice so as to improve diagnosis and surgical treatment of ischemic intestinal lesions.
Purpose: to fi nd the duration of hypolipidemic effect after the course of intravenous laser therapy in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) and lipid metabolism disorders resistant to hypolipidemic pharmacotherapy.
Patients and methods. 40 patients with CAD and lipid metabolism disorders (LMD) resistant to hypolipidemic drugs were enrolled in the trial. Patients were divided into two comparable groups depending on the curative technique: 20 patients from Group 1 (main group) had intravenous laser blood irradiation (ILBI) and supportive medicamentous therapy (SMT). 20 patients from Group 2 (control group) had only SMT.
Results and discussion. Initially, patients in both groups had LMD signs despite of hypolipidemic drug therapy: elevated levels of total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), atherogenic index (AI), and reduced high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) compared to normal values. Baseline values in both groups were statistically insignifi cant for TC, HDL-C, LDL-C and AI levels which indicated comparability between the groups. The study results demonstrated that patients in the main lasered group with ILBI course demonstrated much better hypolipidemic effect in 1 and 3 months after the treatment compared to baseline values: signifi cant reduction in TC by 19.1 % and 16.1 %, respectively; signifi cant reduction in LDL-C by 24.1 % and 21.8 %, respectively; signifi cant reduction in AI by 33.7 % and 29.1 %, respectively. Four months after the ILBI course, hypolipidemic effect became signifi cantly less evident, and lipid profi le indicators in the main group returned to baseline levels, except for total cholesterol. Therefore, in 4 months after ILBI course, patients require a repeated laser therapy course. The controls throughout the observation period had no signifi cant positive dynamics compared to baseline values.
Conclusion. In patients with CAD and LMD resistant to hypolipidemic drugs, ILBI therapy corrects LMD. It has been demonstrated by the signifi cant reduction in TC, LDL-C, and AI levels, as well as by increased HDL-C level, although lipid profi le parameters did not reach their normal or target values. The obtained positive effect persisted for 3 months after the course of laser therapy. After that, ILBI positive effect gradually went down, except the total cholesterol. That is why, in four months patients require a repeat course of laser therapy. To achieve a full hypolipidemic effect in this category of patient, it is necessary to develop and incorporate other non-drug curative techniques.
Purpose. To determine which is the level of probability of damage detection (PDD) by shortwave autofl uorescence (AF) to achieve clinical results in the treatment of central serous chorioretinopathy (CSCR) using the technology of selective micropulse individual retinal therapy (SMIRT).
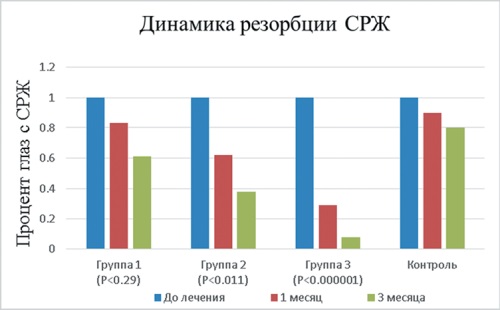
Material and methods. 83 patients (83 eyes) with acute CSCR, aged 30–65, type 1–4 by the Fitzpatrick scale, were under the observation. Patients were divided into four groups. Selective micropulse mode without preliminary testing on Iridex IQ 577 laser system (50–150 μs, 0.5–5 %, 10–50 ms (1–5 pulses), 1.0–2.0 W, 100 μm) was used to treat CSCR in patients from Groups 1, 2 and 3. Parameters to predict the effective PDD levels by AF data were calculated using formulas taking into account patient’s age and type of appearance. In Group 1, parameters for treatment that corresponded to PDD level equal to 50 % were used; in Group 2 – to PDD level of 70 %, and in Group 3 – to PDD level of 90 %. Laser spots were applied close to each other, completely covering detachment areas and RPE defects. In Group 4 (controls), no CSCR treatment was performed.
Results. In Group 1, one month after the treatment complete resorption of subretinal fl uid (SF) was seen in 3 eyes (16.67 %), and three months later – in 7 eyes (38.89 %) (p < 0.29). In Group 2, in one month complete SF resorption was observed in 8 eyes (38.1 %), and in three months – in 13 patients (61.9 %) (p < 0.011). In Group 3, complete SF resorption was observed in 17 patients (70.83 %) in one month after laser treatment, and three months later – in 22 patients (91.67 %) (p < 0.0008). In the control group, during one month follow-up, complete SF resorption was seen in 2 patients (10 %), and during 3-month follow-up – in 4 patients (20 %).
Conclusion. High clinical effectiveness of CSCR treatment with SMIRT technology is achieved when using parameters that correspond to PDD level by AF data of 90 %.
REVIEWS
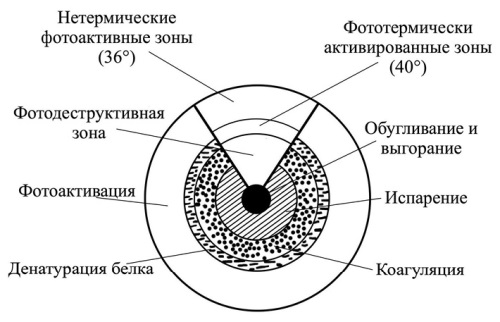
The article presents a review and the analysis of data found in the foreign and domestic literature on features of wound healing in laser skin wounds using morphological and functional test fi ndings. Assessment of foreign and domestic experience allows to defi ne optimal parameters for better therapeutic effect of laser light irradiation of the skin.
A CLINICAL OBSERVATION
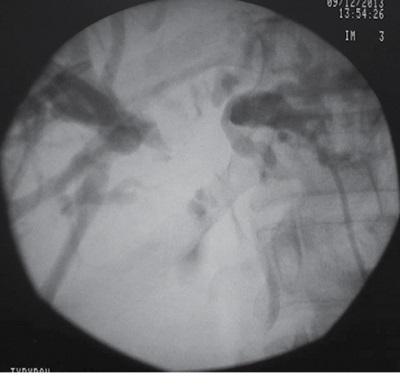
One of the diseases of the biliary area accompanied with the obstructive jaundice syndrome is a portal cholangiocarcinoma or the Klatskin tumor. The authors assess the liver functional state in a patient with portal cholangiocarcinoma using the wedge-shaped dehydration. After diagnosing the Klatskin tumor type III by the Bismuth-Corlette scale and obstructive jaundice, the patient underwent separate external percutaneous transhepatic cholangiostomy of the right and left hepatic ducts under ultrasound and X-ray control. While making the primary percutaneous access to the biliary tract, and every three days after, the researchers studied crystallographic properties of the bile from the right and left liver lobes using the wedge-shaped dehydration method. This examination showed that the left lobe of the liver had more severe dysfunction disorders than the right one. The obtained information, laboratory and instrumental fi ndings were used to choose further management tactics and surgical modality in the described patient. The presented clinical case demonstrates the effectiveness of wedge-shaped dehydration in the dynamic assessment of liver metabolism and a possible effective application of the discussed technique in the management algorithm of patients with obstructive jaundice associated with a portal cholangiocarcinoma.
ISSN 2686-8644 (Online)