ORIGINAL RESEARCHES
Purpose: to study the effectiveness of photodynamic therapy in combination with diathermoelectroconization in the treatment of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer.
Materials and methods. The study included 108 patients aged 33.13 ± 1.18 years. Human papillomavirus was detected in all patients. The study group consisted of 62 patients with cervical diseases. The fi rst subgroup included 28 patients with moderate to severe cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and pT1AN0M0 cervical cancer who underwent diathermoelectroconization and photodynamic therapy. The second subgroup included 34 patients with severe cervical intraepithelial neoplasia who underwent only cervical diathermoelectroconization. The control group included 46 patients with unchanged cervix. To carry out fl uorescent diagnostics and photodynamic therapy, the patients of the fi rst subgroup were intravenously injected with a solution of photosensitizer “Fotoditazin” (“Vetagrand”, Russia) at a dose of 0.8–1.2 mg/kg. Three hours later, using the AFS device (“Polironik”, Russia), fl uorescent diagnostics was performed followed by photodynamic therapy with an ALHT-ELOMED laser (“Elomed”, Russia) in continuous mode. The wavelength was 662 nm, the output power – 3 W, the radiation dose – 200–300 J/cm2 for the cervix and 100–125 J/cm2 – for the cervical canal. All patients underwent complex antiviral therapy.
Results. All patients after photodynamic therapy showed complete eradication of human papillomavirus and regression of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Morphological studies have shown that the effectiveness of combined treatment of moderate and severe cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, reaching 100 %, was higher than with the use of diathermoelectroconization alone (95 %). There were no recurrences of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer after combined treatment.
Conclusion. Photodynamic therapy of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer is a highly effective method.
Purpose. To study outcomes after the minimally invasive treatment of combined hemorrhoids.
Material and methods. Two hundred and three patients with combined hemorrhoids were included in the study. Patients of the main group (n = 101) had laser coagulation of internal hemorrhoids; patients of the control group (n = 102) – ligation of internal hemorrhoids. Then, excision of external hemorrhoids was made in both groups.
Results. The intensity of postoperative pain syndrome decreased more rapidly in patients from the main group comparing to the controls. The number of early postoperative complications in patients of the main group was 2 times less than in the controls. Relapse of the disease one year after the treatment was seen in 5.94 % of patients of the main group and in 22.55 % of the controls.
Conclusion. Laser coagulation of internal hemorrhoids followed by the excision of external ones in patients with combined hemorrhoids can improve outcomes and reduce the number of relapses.
The researchers applied light-oxygen therapy (LOT) in a patient with plaque psoriasis. Diode laser “Super Seb” with wavelength 1265 nm (manufactured by LLC “New Surgical Technologies”, Moscow) was used as a source of laser light: radiation power – 1.2 Wt, power density – 1.06 W/cm2, exposure dose – 191 J/cm2. Sessions were performed 2 times a week with an interval of 3–4 days. After the treatment (3 sessions) a complete clinical remission was achieved.
Purpose: to study the effectiveness of surgical treatment of patients with snoring and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome using TruBlue laser light.
Material and methods. Forty patients suffering of snoring and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome were taken into the study. Outcomes of their treatment are described in the present article. All patients had surgical interventions in the volume of uvulopalatoplasty performed with blue TruBlue laser light, wavelength 445 ± 5 nm (main group – 18 patients) and with Surgitron radio wave apparatus (control group – 22 patients). An objective assessment of respiratory disorders during sleep was done with Apnea Link Air respiratory monitoring system; the obtained fi ndings showed that most of the patients in both groups had snoring without apnea (44.4 and 45.4 %); the obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in them was of mild (38.9 and 36.4 %, correspondingly) and of moderate form (16.7 and 18.2 %, correspondingly).
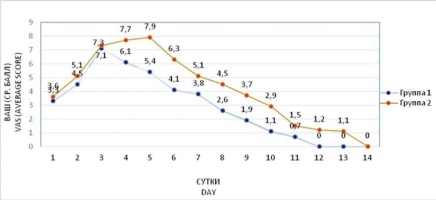
Results. Intraoperative blood loss was less in the main group 1 (2.3 ± 1.1 ml) than in the controls (7.1 ± 1.4 ml). In the postoperative period, patients of the main group had less points (7.1 ± 1.4 by the visual-analog scale) and less prolonged pain syndrome (up to 12 days) than in the control group (7.9 ± 1.2 points, up to 14 days). The subjective positive assessment of symptoms (decreased snoring, daytime sleepiness) was registered in both groups. Respiratory monitoring revealed no deterioration in sleep breathing parameters; decreased apnea/hypopnea index was noted in all observations; however, mild obstructive sleep apnea syndrome was detected in patients in both groups (27.8 and 22.7 %) one month after the surgical treatment.
Conclusion. TruBlue laser light applied in the snoring and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome has been shown to be effective, causing less pronounced blood loss and pain syndrome, if to compare to the radio wave technique.
Purpose: to assess the effectiveness of carbon dioxide laser light in the treatment of benign skin neoplasms.
Material and methods. The researchers have analyzed outcomes in 1394 patients treated for benign skin neoplasms. In the main group (n = 1184), laser photocoagulation (vaporization) and laser photohydraulic preparation were applied. Laser surgical devices “Lancet-1” and “Lancet-2” in continuous and pulsed modes, power up to 20 W, focused beam up to 1 mm were used. In the control group (n = 210), traditional techniques (excision and electrocoagulation) were applied.
Results. High effi ciency of CO2 laser light for the removal of benign skin neoplasms has been confi rmed. Such a technique has a minimal rate of complications and relapses and satisfactory aesthetic outcomes, compared to the conventional treatment.
Conclusion. Carbon dioxide laser light is highly effective for treating benign skin neoplasms.
REVIEW
The authors present a review of trials on the effects of irradiation in the blue range of the spectrum emitted by optoelectronic devices on the human body. Light therapy in the blue range is scientifi cally grounded and inexpensive type of care. The blue-band optical radiation has a high
therapeutic effi cacy in the absence of adverse reactions and complications.
OBITUARY
ISSN 2686-8644 (Online)